Despite the important role calories play in our daily lives, they are often misunderstood. While some people ignore calories completely, others are afraid of them. In reality, calories are simply a measure of energy and are neither good nor bad on their own. What truly matters is how to control calorie intake for men and women by understanding how many calories the body needs, where those calories come from, and how efficiently the body uses them.
Because men and women have different body compositions, hormonal functions, and energy requirements, their calorie needs also differ. Consuming too many or too few calories can negatively affect energy levels, weight, metabolism, and overall health.
This comprehensive guide explains what calories are, their benefits, the potential damages of excessive or insufficient calorie intake, and practical ways men and women can manage their calorie consumption effectively—without harming their health or lifestyle.

What Are Calories?
A calorie is a unit of energy. Nutritional calories are essentially the energy that your body derives from food and drink. This is the energy that your body uses to:
- Breathe
- Circulate blood,
- Break down food
- Work muscles.
- Maintain a steady body temperature.
Whereas calories exist in all types of food, the difference in caloric value of one food over another mainly depends on their nutritional composition. Foods packed with nutrients like fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals are definitely the heroes when compared to the empty-calorie foods, which are simply high in calories and low in nutrients.
Benefits of Calories for the Human Body
Calories are essential for survival. Without enough calories, the body cannot function properly.
1. Calories Provide Energy
All daily activities, like walking, working, and vigorous exercise, are driven by calories. Having the right number of calories prevents chronic tiredness and promotes steady energy levels.
2. Support Metabolism
Calories are required for your metabolism to carry out essential functions such as digestion, circulation, and cell repair. Over time, a low-calorie diet may decrease metabolism.
3. Maintain Hormonal Balance
Obtaining sufficient calories promotes the production of hormones. Because extreme calorie restriction can interfere with menstrual cycles and fertility, this is especially crucial for women.
4. Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein-rich calories help repair tissues and build muscle. This benefit is crucial for:
- Men aiming for muscle growth
- Women maintaining lean muscle and bone strength
Damages of Excess Calories
While calories are necessary, consuming more calories than your body needs can lead to serious health problems.

1. Weight Gain and Obesity
Extra calories are stored as fat. Over time, a consistent calorie surplus leads to:
- Weight gain
- Belly fat
- Obesity
2. Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases
Excess calorie intake—especially from sugary and processed foods—raises the risk of:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Fatty liver disease
3. Low Energy and Poor Mental Health
Ironically, overeating can make you feel tired. Junk-food calories cause blood sugar spikes, followed by crashes that result in:
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
- Poor concentration
Damages of Too Few Calories
Eating too few calories is just as harmful as eating too many.
1. Nutrient Deficiencies
Low-calorie diets are frequently low in vital nutrients, which can result in:
- Low immunity
- Loss of hair
- brittle nails
- Anemia
2. Hormonal Issues (More Often in Women)
Having fewer calories may throw off progesterone and estrogen levels, which can lead to:
- Periods that are irregular
- Difficulties with fertility
- Loss of bone
3. Weakness and Loss of Muscle (More Common in Men)
The body burns muscle for energy when calorie intake is too low, which lowers metabolic rate and strength.
Daily Calorie Needs for Men and Women
Calorie requirements vary based on age, activity level, and body composition.

Average Daily Calorie Needs for Men
Sedentary: 2,000–2,200 calories
Moderately active: 2,400–2,600 calories
Active: 2,800–3,000+ calories
Average Daily Calorie Needs for Women
- Sedentary: 1,600–1,800 calories
- Moderately active: 1,800–2,000 calories
- Active: 2,200–2,400 calories
Men generally need more calories because they have higher muscle mass and metabolic rates.
Calories for Weight Loss, Maintenance, and Weight Gain
Calorie Deficit (For Weight Loss)
A calorie deficit means consuming fewer calories than your body burns. A healthy deficit usually ranges from 300 to 500 calories per day.
Maintenance Calories
Your weight stays steady due to maintenance calories. Unwanted weight gain or loss can be prevented by matching eating and energy expenditure.
Calorie Surplus (For Weight Gain)
A moderate calorie surplus supports muscle gain. Focus on nutrient-dense foods rather than junk calories.
How to Control Calorie Intake for Men and Women
This is the most important part of sustainable health.
1. Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods
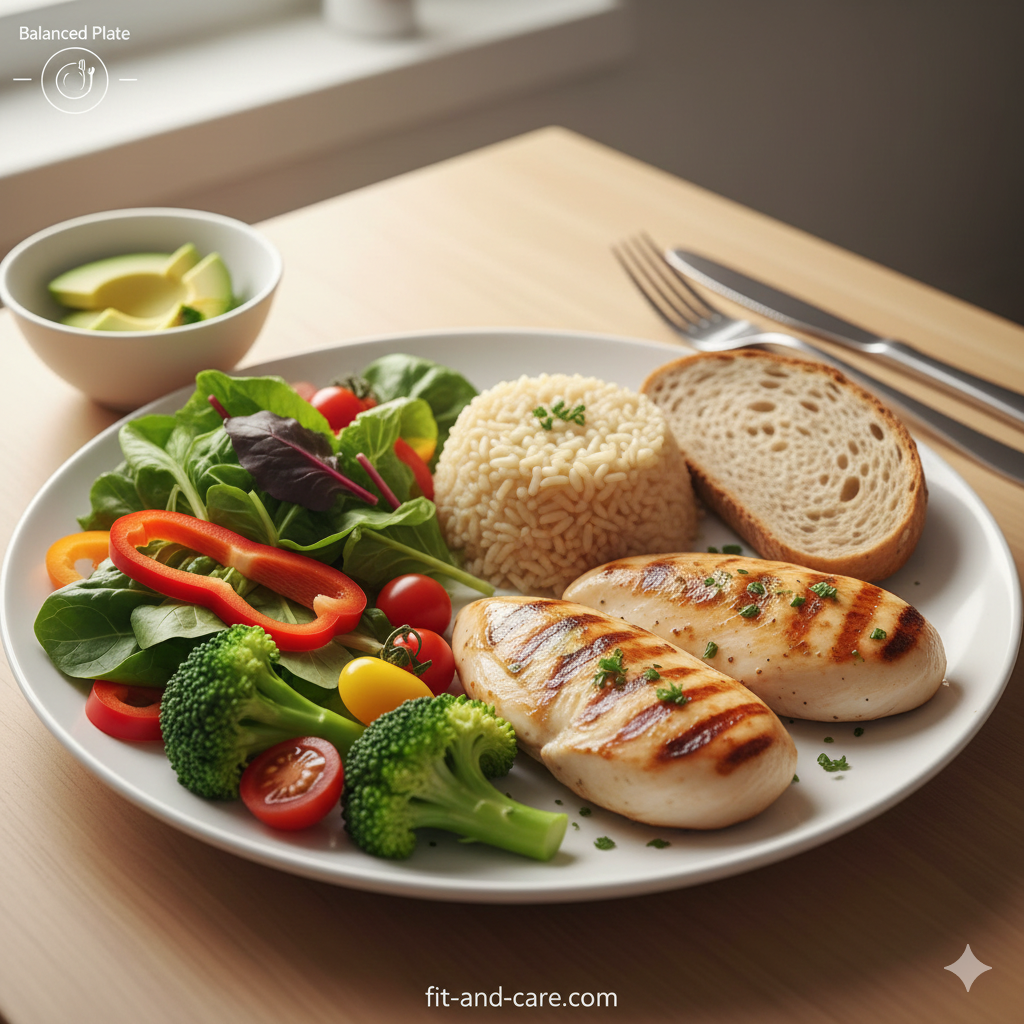

Fill your plate with:
- Vegetables and fruits
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
- Healthy fats
These foods keep you full while controlling calorie intake.
2. Control Portion Sizes
Eating healthy foods in huge portions still increases calorie intake. Visual portion guides can help prevent overeating.
3. Avoid Empty Calories
Limit foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats, such as:
- Sugary drinks
- Fried food
- Packaged snacks
4. Read Nutrition Labels
Understanding serving sizes and calories per portion helps you stay aware of your intake.
5. Plan Meals in Advance
Meal planning prevents impulsive eating and helps maintain calorie balance for busy men and working women.
Calorie Control Tips for Men
- Prioritize protein to preserve muscle mass
- Avoid late-night snacking
- Limit alcohol calories
- Balance strength training with cardio
Calorie Control Tips for Women
- Avoid extreme calorie restriction
- Support hormonal balance with healthy fats
- Eat enough during the menstrual and pregnancy phases
- Focus on consistency rather than perfection
Best Foods for Healthy Calories
- Healthy fats: Avocados, nuts, olive oil
- Complex carbohydrates: Brown rice, oats, quinoa
- Lean proteins: Eggs, chicken, fish, legumes
These foods provide long-lasting energy without unnecessary damage.
Common Myths About Calories
Myth 1: All calories are bad
Truth: Quality matters as much as quantity.
Myth 2: Skipping meals saves calories
Truth: It often leads to overeating later.
Myth 3: Women should eat very low calories
Truth: Extreme restriction harms hormones and metabolism.
Conclusion
Life, energy, and overall wellness all rely on calories, but balance is essential. To maintain their energy, hormonal health, and body weight, both men and women need the right amount of calories from nutritious sources. Stay away from extremes, focus on eating high-quality foods, and check your intake with smart tools like MyFitnessPal.
Knowing how to control calories is about making wise, healthy choices for long-term well-being, not about limiting.
You can also read an article on Natural foods

1 thought on “Calories: Benefits, Damages & How to Control Calorie Intake for Men and Women”